| To Duval Family Home Page | South America |
| To Chris Home Page | Hispano-America |
| To Earth (Geography Home Page) | Chile and its Antarctic claims |
Chile
In Chile's center, a coastal range bounds a fertile plateau's west. Beyond this valley's east edge several lakes are found among the Andes.
Yet further south, the mountains are separated by sea channels, and the western ones are on islands. The Andes end as an eastward curl on the south of the large southern island, Isla Grande de Tierra Del Fuego (Great Island of the Land of Fire),
Tourists visit Lauca National Park in the north Andes; Pucón in the volcanic north Andes; Torres del Paine National Park in the southern transition from high forest to high steppe; Valle de la Luna in the Atacama desert; the San Rafael Glacier in the northern Patagonian area of southern Chile; and los Penguines (penguins) National Monument on Magdalena and Marta Islands.

Almost 16 million live in Chile, the great majority speaking Spanish, and almost everyone a Christian. Almost nine in ten are Roman Catholics; the rest Protestants.
Santiago is the only city with a million or more residents. There are important airports at Santiago; near Antogoasta (population 285 thousand;
Tourists visit the old urban (Castro) and rural churches of Chiloé Island,
When the Spanish arrived in the 16th century, the Incan Empire controlled northern Chile. They introduced the Quechua language. Aymara may have already been spoken in the Puna Atacama, or it may have spread under the Incans. Further south, Araucanian
Hints of pre-Christian religions can be found in festivals for the Virgin Mary
Isla de Pascua was the easternmost limit of long term settlement by Polynesians, and the moai they erected are both a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a tourist attraction.
northeast, from the north
east, from the north
east
east and north from the insular south
east, from the south of the mainland
south of the insular south
west
northwest, from the north
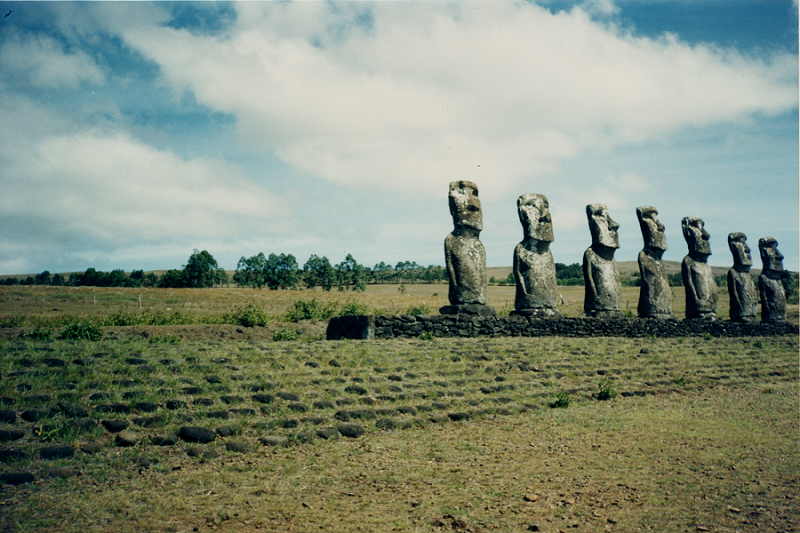

Moai, Isla de Pascua (Rapa Nui), Valparaíso Region, Chile
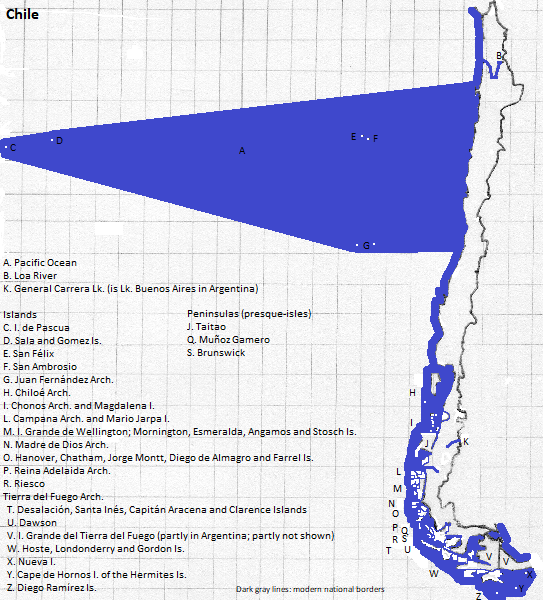
1. Also included are several Pacific islands: San Félix, the San Ambrosio Islands, the Juan Fernández Archipelago, Isla de Pascua (Easter Island, also known as Rapa Nui), and the Sala and Gómez Islands. Excluded is Antártica Chilena (Chile's claim in Antarctica), which is part of the región of Magallanes y Antártica Chilena. The rest of that region is in South America and is included.
2. South America's largest island.
3. http://www.touropia.com/tourist-attractions-in-chile/, accessed June 21, 2018.
4. 2012 figure from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_cities_in_Chile, accessed June 21, 2018.
5. 2013 All Flights table (limited by me to rows for over one million passengers) in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_the_busiest_airports_in_Chile, June 21, 2018.
6. Or Mapudungan.
7. Some say they can be grouped with Araucanian as the Araucanian-Chan Family. Yet more ambitiously, some would group them with many American languages as Amerindian.
8. The mother of the Christian man-god.