There are numerous fresh water lakes in the south and some large reservoirs further north.
The most important rivers are the Colorado,
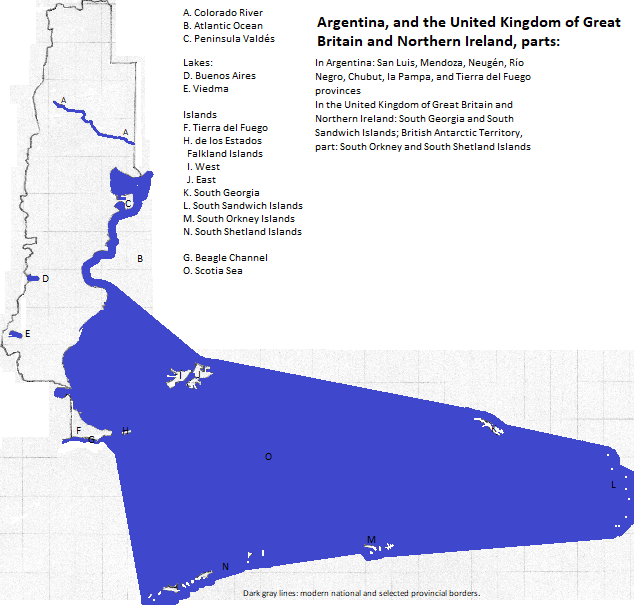
UNESCO honors two natural areas as World Heritage Sites: los Glaciares in Santa Cruz Province; and the Valdés Peninsula in Chubut Province. Tourists visit Perito Moreno Glacier in los Glaciares National Park as well as the Valdés Peninsula.
Map
Who lives there?
About 4.5 million people live here. More than 19 in 20 speak Spanish as their first language, and almost all are Roman Catholic Christians.
The only city with more than a million residents is Mendoza. Tourists also visit Bariloche on the Negro River in the north center of the province with the river's name (formal city name San Carlos de Bariloche; city population 110 thousand)
Who was there before?
Before the Spanish arrived, everyone spoke languages that a few people group as Amerindian. Language groups were Araucanian and Chon.
The pre-Christian religions of Tierra del Fuego believed in a supreme deity, albeit--at least in the case of the Selk'nam--an inactive one.
UNESCO honors two areas that preserve pre-Columbian cultural remains as World Heritage Sites: Cueva de las Manos, Río Pinturas in Santa Cruz Province; and Qhapaq Ñan, Andean Road System, in Mendoza Province and beyond.
Around the Area
Around the mainland:
northeast, from the north
east, from the south
south, from the south, and west