| To Duval Family Home Page | South America |
| To Chris Home Page | Hispano-America |
| To Earth (Geography Home Page) | Perú |
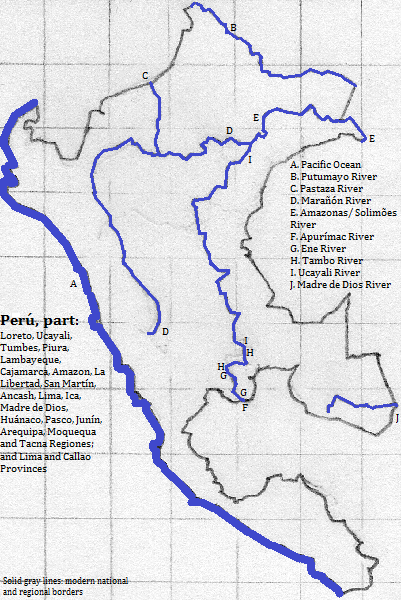
East and south of Ecuador is Perú, part of which is in this area. Here the three ranges of the Andes again become distinct, the coastal plain dries out and the principle headwaters
Two UNESCO World Heritage Sites honoring nature are in this area: Huascarán National Park in Ancash Región and Río Abiseo National Park in San Martín Región; Río Abiseo is also important to archaeology.

This is one part of a large area of the Americas where Spanish and Roman Catholic Christianity represent the majority.
Lima is the only city with over a million residents. Other cities of note are Trujillo, Arequipa, Ica and Iquitos.
The important
A sampling of pre-Columbian languages follows: I. Jivaroan languages were spoken in Loreto and Amazon regiones. II. Zaparoan languages and III. Yagua were also spoken in Loreto. IV. Panoan languages were spoken in Ucayali and Madre de Dios regiones. V. Chimu, now extinct, was spoken along Perú's central coast where the Chimor Empire flourished from the early 11th to the end of the 13th centuries. VI. The Incan Empire spread Quechua through Perú and beyond, wholly or partly displacing earlier languages. The language originated in the highland part of this area and spread southeast, beyond this area, to what became the center of the Incan state. VII. Tupi languages and the closely related Guarani were spoken in some areas near Brazil and Paraguay (e.g., Loreto).
The best known religions were two: I. The iconography of the Weeping Sun God spread from south of the area of coastal and central highland Perú. II. The state-sponsored Incan religion, centered in other parts of Perú, embraced a pantheon of gods, including Inti and Viracocha.
There are six UNESCO World Heritge Sites honoring culture: Chan Chan Archaeological Zone in La Libertad Región; Chavín (Archaeological) Site in Ancash Región; Historic Centre of Lima; Historic Centre of the City of Arequipa; Lines and Geoglyphs of Nasca and Pampas de Jumana in Ica Región and the Sacred City of Caral-Supe in Lima Región. Tourists visit Chan Chan; the beach resort of Máncora in Piura Región; the Nasca Lines; the Colca Canyon in Arequipa Región; and some of the cities.

Sunset over the Amazonas River, Perú
north from northernmost Loreto, Perú
northeast
east of Loreto and Ucayali and north of Madre de Dios
southeast of Madre de Dios
south of Junín and Ucayali; southwest and south of Madre de Dios; northeast of Tacna, Moquegua and Ica; northeast and north of Arequipa; and southeast of Lima
southwest
northwest
1. Amazonas in Spanish.
2. Translates as The Liberty.
3. Translates as Saint or Holy.
4. It is said to translate from an indiginous language as 'Speaker'.
5. The Ucayali and the Maroñón. The source of the Purus, another Amazon tributary and South America's third or fourth longest river, is in Perú's eastern lowland.
6. Occidental in Spanish.
7. Translates as Snowy-peak.
8. Oriental in Spanish.
9. The Times Atlas of the Oceans (Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, 1983), "commodity loading ports" map.
10. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_natural_gas_fields, accessed 2/25/2014.
11. http://www.touropia.com/tourist-attractions-in-peru/, accessed 2/25/2014.